Introduction
Bambusa Balcooa, commonly known as Beema Bamboo, is a tropical clumping bamboo species native to the Indian subcontinent, particularly in regions like India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. This bamboo species is celebrated for its robust growth, high biomass production, and significant environmental benefits.

History and Origins
Ancient Roots
Bambusa Balcooa has a rich history, originating in tropical regions of Southeast Asia. It's been used for centuries in traditional construction and craft, particularly in rural areas where its durability and flexibility were highly valued.
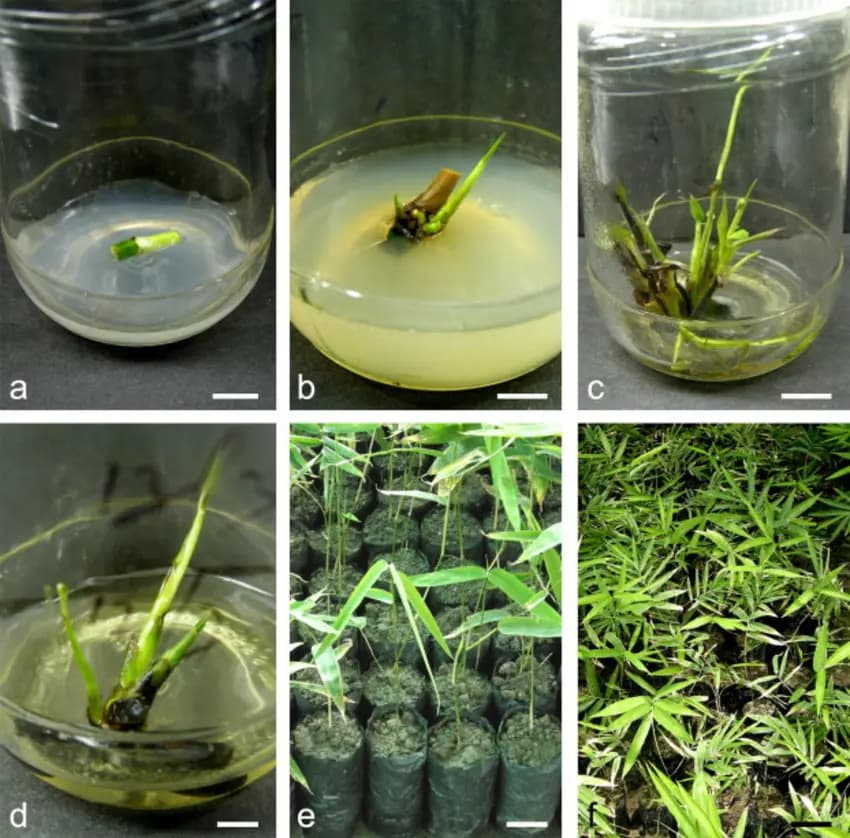
Modern Use and Tissue Culture
Modern tissue culture techniques have allowed for the mass production of Bambusa Balcooa. These methods ensure healthy, disease-free plants that grow uniformly. Tissue culture involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich medium under sterile conditions, allowing for rapid propagation.

Identification and Unique Characteristics
How to Identify Bambusa Balcooa
- Height: Typically grows between 15-25 meters.
- Culms: Thick and green, turning yellowish with age. Diameter ranges from 10 to 15 cm.
- Leaves: Long and narrow, measuring around 15-30 cm in length and 2-5 cm in width.

Distinguishing Features
Unlike other bamboo species, Bambusa Balcooa has denser culms and fewer branches, making it ideal for structural uses. It has a higher tensile strength, making it a preferred choice for construction and scaffolding.
Maintenance and Growth
Maintenance Schedule
- Watering: Requires regular watering, especially in the first two years.
- Fertilization: Use organic fertilizers biannually.
- Pruning: Remove dead or weak culms annually to promote healthy growth.

Optimal Conditions
Bambusa Balcooa thrives in well-drained soil with plenty of sunlight. It can tolerate a range of temperatures but prefers warm climates. Regular monitoring for pests and diseases ensures healthy growth.
Carbon Sequestration Benefits
Environmental Impact
Bambusa Balcooa is exceptional for carbon sequestration, absorbing up to 12 tons of CO2 per hectare annually. This makes it a vital tool in combating climate change.
Numbers and Impact
Studies show that planting Bambusa Balcooa can significantly reduce carbon footprints, contributing to a greener planet. For example, a plantation of 100 hectares can sequester 1,200 tons of CO2 annually.
Differences from Native Species
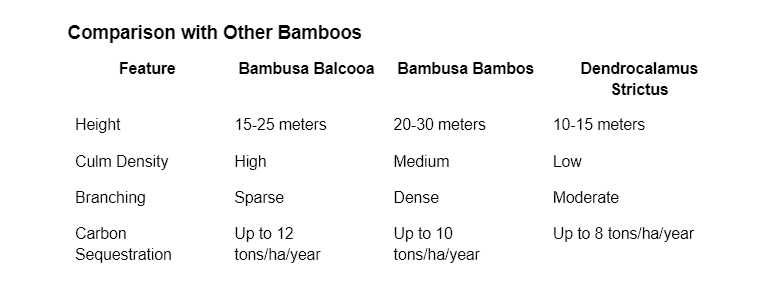
Native vs. Cultivated Benefits
While native species like Bambusa Bambos have their advantages, Bambusa Balcooa's superior strength and environmental benefits make it a preferred choice for many projects.

Notable Projects in India
Nationwide Impact
Across India, Bambusa Balcooa is being used in various reforestation and construction projects, providing sustainable solutions. These projects aim to enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, and offer economic benefits to local communities.
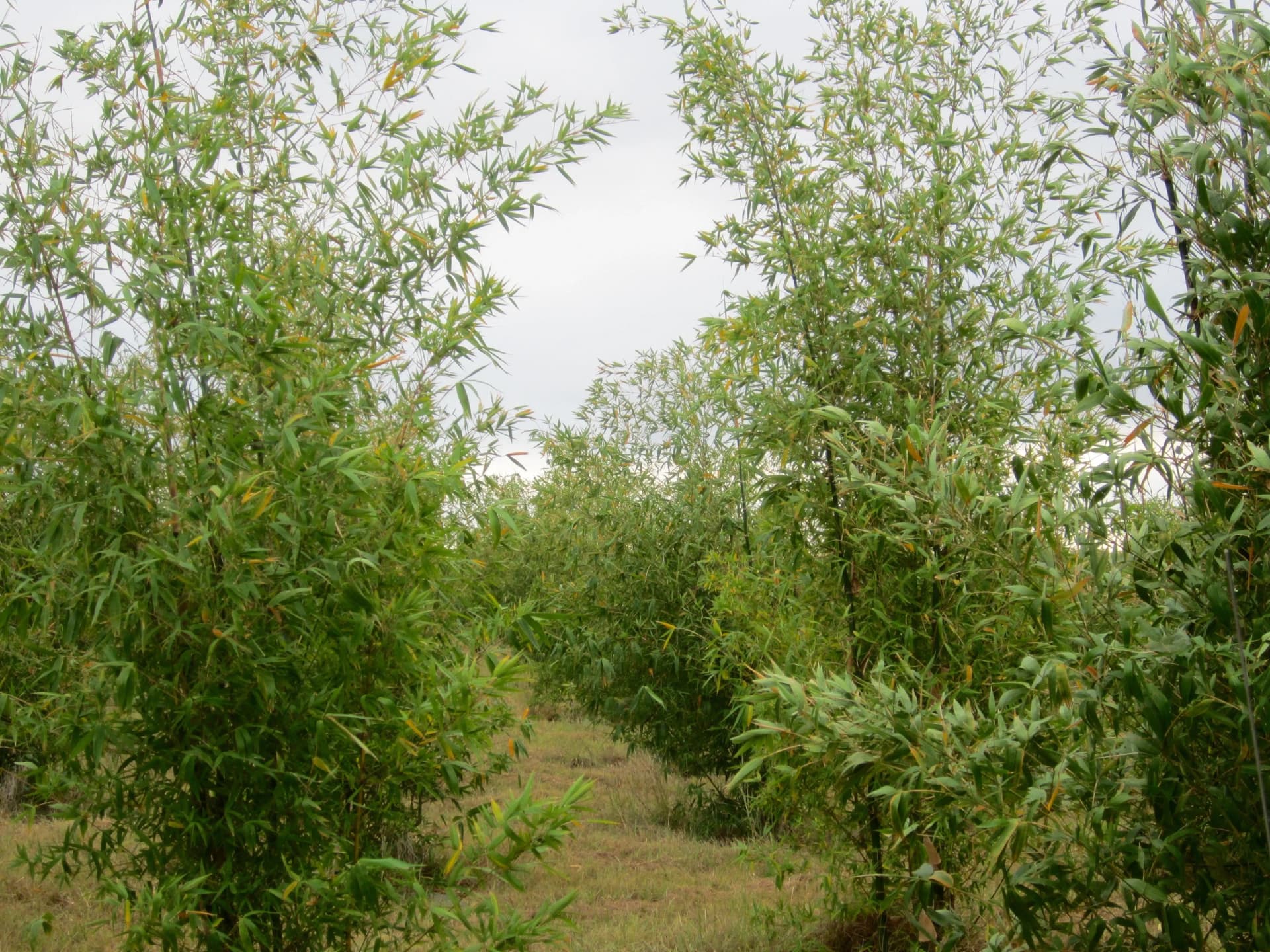

CATCH Foundation's Project in Manesar, Haryana
In one of the largest plantations in Delhi NCR, the CATCH Foundation, with CSR collaboration from Sona Comstar, planted 20,000 Bambusa Balcooa in Manesar, Haryana. This project aims to improve air quality and provide sustainable resources.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Economic Uses
Bambusa Balcooa provides numerous economic benefits. It can be harvested for various products, including construction materials, paper, furniture, textiles, and biofuel. Its rapid growth and high biomass yield make it a sustainable resource.
Environmental Benefits
The extensive root system of Bambusa Balcooa helps prevent soil erosion, making it beneficial for planting on slopes and degraded lands. Its ability to regenerate quickly after harvesting ensures a continuous supply of resources.

Detailed Comparison with Native Species
Growth Rate and Biomass
• Bambusa Balcooa: Rapid growth, high biomass yield of approximately 25-30 kg of dry biomass per tree per year.
• Native Species: Generally slower growth, lower biomass yield of around 10-15 kg per bamboo per year.
Carbon Sequestration
• Bambusa Balcooa: Sequesters 400-450 kg/year/per bamboo.
• Native Species: Sequesters 40-42 kg/year/per tree.
Ecological Impact
• Bambusa Balcooa: Can outcompete local flora.
• Native Species: Supports local biodiversity and is adapted to local ecosystems.
Economic Uses
• Bambusa Balcooa: Versatile for construction, paper, textiles, and biofuel.
• Native Species: Varies but includes traditional medicine, timber, and food products.
Water and Nutrient Needs
• Bambusa Balcooa: Requires significant water and nutrients.
•Native Species: Lower requirements, adapted to local conditions.
Longevity and Lifecycle
• Bambusa Balcooa: Matures faster and can be harvested and regrown in 3-5 years.
• Native Species: Longer lifecycle with slow maturation.

Conclusion
Bambusa Balcooa is not just another bamboo species; it's a powerhouse of benefits, from environmental impact to structural applications. With its rapid growth, high carbon sequestration capabilities, and robust nature, it stands out as a sustainable solution for modern challenges.
References
Source 1: Carbon Sequestration Study
Source 2: CATCH Foundation Project
Source 3: Bambusa Balcooa on Wikipedia
Source 4: Bamboo Tissue Culture
By following these guidelines and leveraging Bambusa Balcooa, we can move towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
